Objective
Percutaneous laser disk decompression (PLDD) is an effective treatment for bulging or protruding disk. The aim of this study was to present a method of PLDD for cervical disk hernia under CT guidance and to evaluate the efficacy and safety of this procedure.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
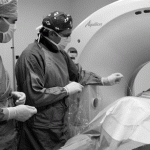
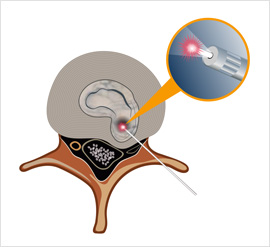
Seven patients with radiculalgia caused by cervical disk hernia were treated overnight by PLDD. A laser fiber was inserted through an 18 G needle into the target disk under CT guidance. A Nd-Yag laser (1,064 nm) was used for ablation. A CT scan was obtained every 60 joule (J) at the slice of the target disk to visualize the vaporized area during the procedure. The Japan Orthopedic Association (JOA) score of cervical radiculopathy (full score 15) and MacNab criteria were used for assessment of treatment response.
RESULTS
Puncture of the needle to the target disk was safely performed under CT guidance. The total dosage of laser ablation ranged from 120 to 500 J (average, 266 J). The overall success rate according to MacNab criteria was good in all cases. No complications were observed in our series
CONCLUSION
The CT-guided technique provides safe, accurate PLDD for cervical disk hernia. PLDD for cervical disk hernia shows promise in the management of radiculalgia.
Refrence
CT-guided percutaneous laser disk decompression (PLDD) for cervical disk hernia.
Harada J1, Dohi M, Fukuda K, Nakazaki H, Koyama T, Abe T.