Overview
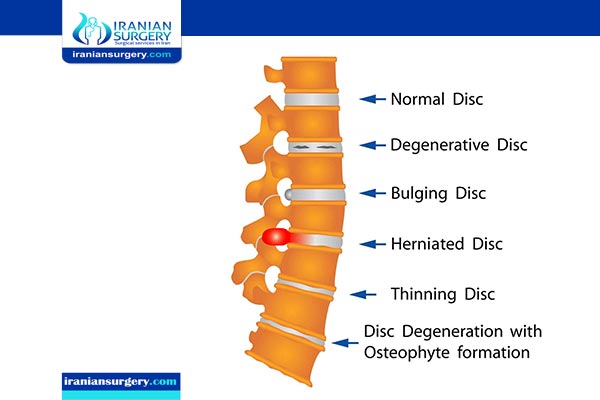
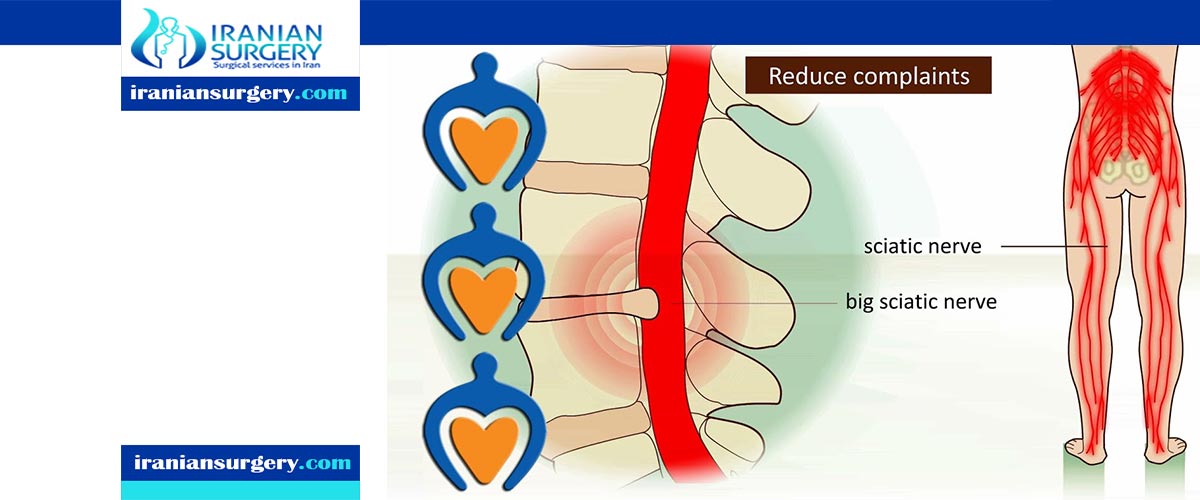
A herniated disk in Iran refers to a problem with one of the rubbery cushions (disks) between the individual bones (vertebrae) that stack up to make your spine.
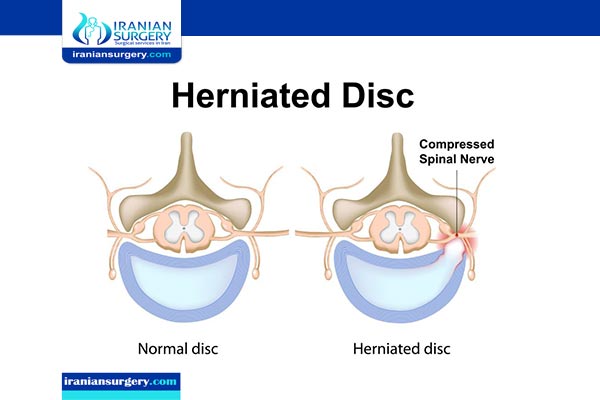
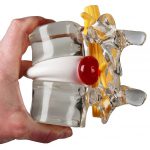
A spinal disk is a little like a jelly donut, with a softer center encased within a tougher exterior. Sometimes called a slipped disk or a ruptured disk, a herniated disk occurs when some of the softer “jelly” pushes out through a tear in the tougher exterior.
A herniated disk can press on the nerves in your spine and cause pain, weakness, and numbness in your neck, back, arms, and legs. Sometimes these symptoms can be severe enough to disrupt your life.
Risk factors
Factors increasing your risk of a herniated disk may include:
. Weight. Excess body weight causes extra stress on the disks in your lower back.
. Occupation. People with physically demanding jobs have a greater risk of back problems. Repetitive lifting, pulling, pushing, bending sideways and twisting also may increase your risk of a herniated disk.
. Genetics. Some people inherit a predisposition to developing a herniated disk.
. Unsafe lifting technique. People should always apply force from the legs, not the back, when lifting heavy items. Incorrect technique can lead to a herniated disk.
. Driving often. A combination of being seated for long periods and the vibrations and movements of the car can damage the disks and spinal structure.
. Sedentary lifestyle. A lack of exercise can lead to a herniated disk.
. Smoking. This might reduce oxygen supply to the disks and lead to a grinding-down of the tissue.
Treatment
Non-Surgical Treatments
The initial treatment for a herniated disc is usually conservative and nonsurgical. A doctor may advise the patient to maintain a low, painless activity level for a few days to several weeks. This helps the spinal nerve inflammation to decrease. Bedrest is not recommended.
A herniated disc is frequently treated with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medication, if the pain is only mild to moderate. An epidural steroid injection may be performed utilizing a spinal needle under X-ray guidance to direct the medication to the exact level of the disc herniation.
The doctor may recommend physical therapy. The therapist will perform an in-depth evaluation, which, combined with the doctor’s diagnosis, dictates a treatment specifically designed for patients with herniated discs. Therapy may include pelvic traction, gentle massage, ice and heat therapy, ultrasound, electrical muscle stimulation and stretching exercises. Pain medication and muscle relaxants may also be beneficial in conjunction with physical therapy.
Surgery
Most people with a herniated disk don’t need surgery. Rest and other treatments should start to improve your symptoms within 4 to 6 weeks. But if your pain doesn’t improve, surgery might be an option.
Talk to your doctor about surgery if:
. You’re not getting relief from pain relievers, injections, and physical therapy.
. Your symptoms keep getting worse.
. You have trouble standing or walking.
. You can’t control your bowels or bladder.